What Are Verbs?
Verbs are made up of one or more “action” words.
TYPES OF VERBS
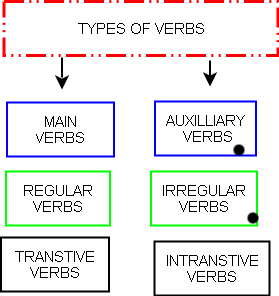
Finite, Non finite / Infinite, Regular, Irregular, Transitive, Intransitive, Auxiliary, Infinitive, Participles
Finite Verbs
Finite verbs are complete verbs, as they have a subject, number and a tense.
Example: He is singing.
“is singing” is a finite verb as it has a subject (he), a number, and a tense (present continuous)
Non Finite/Infinite Verbs
These do not have either a subject, number or definite tense.
Example: asking permission
“asking permission” is a non finite verb as it does not have a subject, number or a definite tense.
Regular Verbs
These are verbs that end in “ed” when they are in the past tense.
Examples: kick, stop, type
These are all regular verbs which end in “ed” when used in the past tense. Kick becomes kicked. Stop becomes stopped. Type becomes typed.
Irregular Verbs
These are verbs that do not end in "d" or “ed” in the past tense.
Examples: run, fight, think
These are all irregular verbs which do not end in “ed” in the past tense. Run becomes ran. Fight becomes fought. Think becomes thought.
Transitive Verbs
These are verbs that have objects. (This means that the action the verb describes is done to something or someone.)
Example: The man kicked the ball.
In this sentence the verb, “kicked” is being done to the object, the ball.
Intransitive Verbs
These are verbs that do not have an object. The action described by the verb is not done to anyone or anything.
Examples: Ducks swim.
Dogs bark.
Babies cry.
Auxiliary Verbs
These are verbs that help to express the meaning of the main verb in a sentence. They are forms of the verb “to be” or the verb “to have”.
Words like: am, is, are, has, have etc. are often used as auxiliary verbs.
Examples: I am running.
She has slept.
He is going.
MODAL VERBS
Modal verbs are a special type of auxiliary verb.
Modal verbs are used to express an attitude towards what is being said or written.
There are two types of modal verbs. These are pure modal and semi-modal verbs.
Pure Modal Verbs
(These are complicated and will only be dealt with very briefly here)
Pure Modal verbs do not change in any way in the past tense.
These always come before the main verb, which in the case of pure modal verbs is always in the bare infinitive form i.e. “run” not “to run”
May, Might, Would, Could, Need, Should, Can, and Should are pure modal verbs.
Examples: He may run home.
He might run home.
He should run home.
He could run home.
Semi Modal Verbs
These are auxiliary (helping) verbs that are usually followed by the full infinitive (e.g. to run).
Examples: ought to, has/have to, able to
Verbs in the Infinitive Form
The infinitive form of the verb is the base form the verb.
It is the form usually found in the dictionary. The infinitive form a verb can always have the word “to” in front of it.
Examples: run, jump, sing, stop, listen, look
Participles
Participles are the endings added to verbs to give the tense of the verb.Participles "take part" or "participate" in the meaning of a verb.
There are two types of participles. These are present participles and past participles.
PRESENT PARTICIPLES
The present participle is the “ing” extension to the verb used for the present continuous tense.
Examples: running, jumping, laughing, singing
Note: Present participles can sometimes be used as adjectives.
Example: The singing boy.
PAST PARTICIPLES
Past participles are the various forms that verbs take in the past perfect tense (when the action of the verb is complete).
They usually come after the words “has” or “have”. For regular verbs this form of the verb ends in d or ed.
Example: We have finished the game.
For irregular verbs the past participle form ends in a number of differnt letters. Some of these are “t”, “en” or “n”.
Example: We have taken the keys.
We have learnt something.
Verbs, Types of verbs, Verbs form
Verbs, Types of verbs, Verbs form